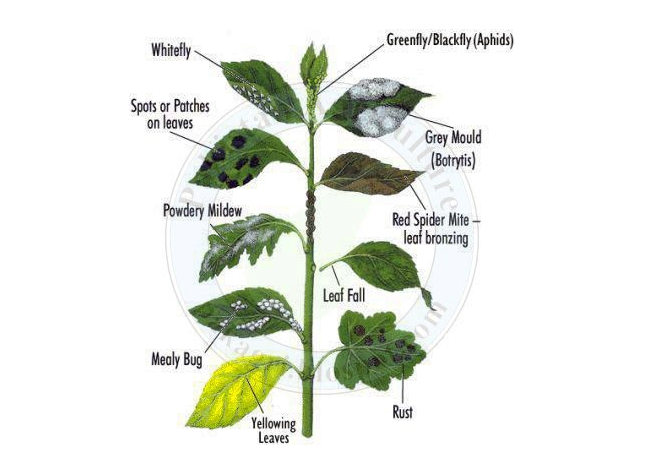
This picture describes the graphic detail of plant Leaves diseases:

White flies – are one of the most bothersome that a gardener can have in their garden. Whether they are on ornamentals or vegetables, white fly control can be tricky and difficult.
Aphids – They are small, soft-bodied insects that can survive in almost any zone. Aphids multiply quickly, so it’s important to get them under control before reproduction starts.
Spots – Pathogen-caused leaf spot diseases, particularly those of stone fruit trees and such vegetables as tomato, pepper and lettuce are of two types, those caused by bacteria and those caused by fungus.
Grey mould – caused by the fungus Botrytis cinerea, is a very common disease, causing a soft decay of plant tissues accompanied by a growth of fuzzy grey-brown mould. It affects many plants, especially those grown under glass where conditions are humid. It is also a common disease of soft fruit, such as gooseberries, strawberries and grapes.
Powdery mildew – There are many different species of the fungal disease powdery mildew, and each species attacks a range of different plants. Unlike many other fungal diseases, powdery mildew thrives in warm, dry climates, though it does require fairly high relative humidity to spread.
See also: Everything you need to know about plant nutrients
- Leaf fall
Leaf bronzing – it refers to the way some leaves or fruit turn purplish or bronze-colored as a result of mineral imbalances, pest feeding, chemicals, environmental conditions, or disease. Bronzed leaves tend to be smaller than normal and the damaged areas are unable to perform photosynthesis.
Rust – Common rust (Phragmidium spp.) is a fungal disease that attacks roses, hollyhocks, snapdragons, daylilies, beans, tomatoes and lawns. It is most often found on mature plants where symptoms appear primarily on the surfaces of lower leaves.
Mealy bug – Found in warmer growing climates, mealybugs are soft-bodied, wingless insects that often appear as white cottony masses on the leaves, stems and fruit of plants. They feed by inserting long sucking mouthparts, called stylets, into plants and drawing sap out of the tissue. Damage is not often significant at low pest levels. However, at higher numbers they can cause leaf yellowing and curling as the plant weakens.
Yellowing of leaves – Plants are susceptible to temperature variations, sensitive to chemicals and excesses of nutrient, require specific soil compositions and pH levels, have varying lighting needs, are prey to certain pests and diseases, and many other factors influence their health. Yellowing leaves on plants can be a sign of any of these out of balance or even certain nutritional or chemical influences.

2 thoughts on “Recognizing Leaf Diseases On Plants”
Bill Absher
(June 12, 2019 - 2:03 pm)Good Morning
Kalule Joseph Solomon
(August 30, 2019 - 12:24 am)Nice information, Thanks a lot please and may i have such information on my e-mail so that i prove my know how. Thanks please